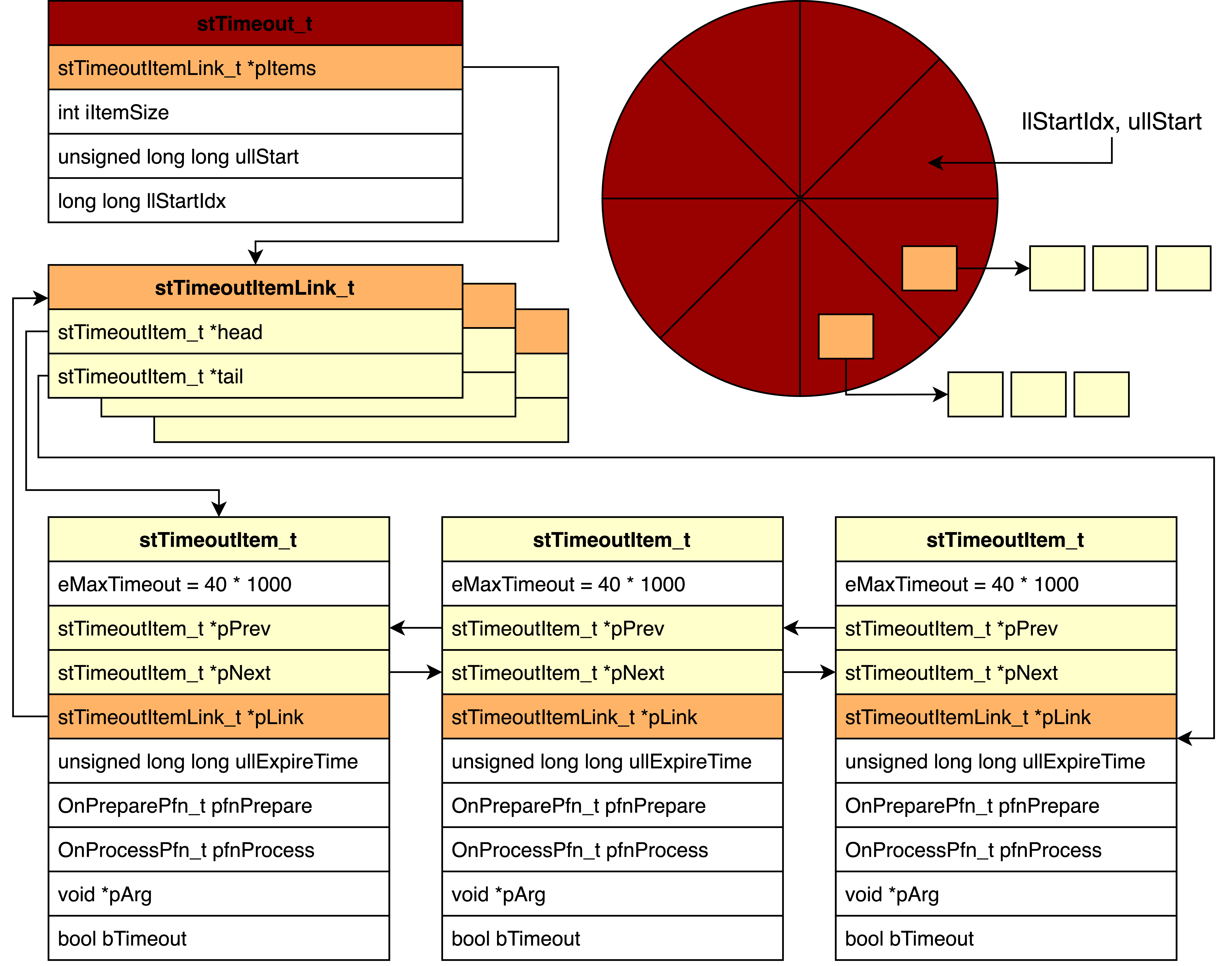
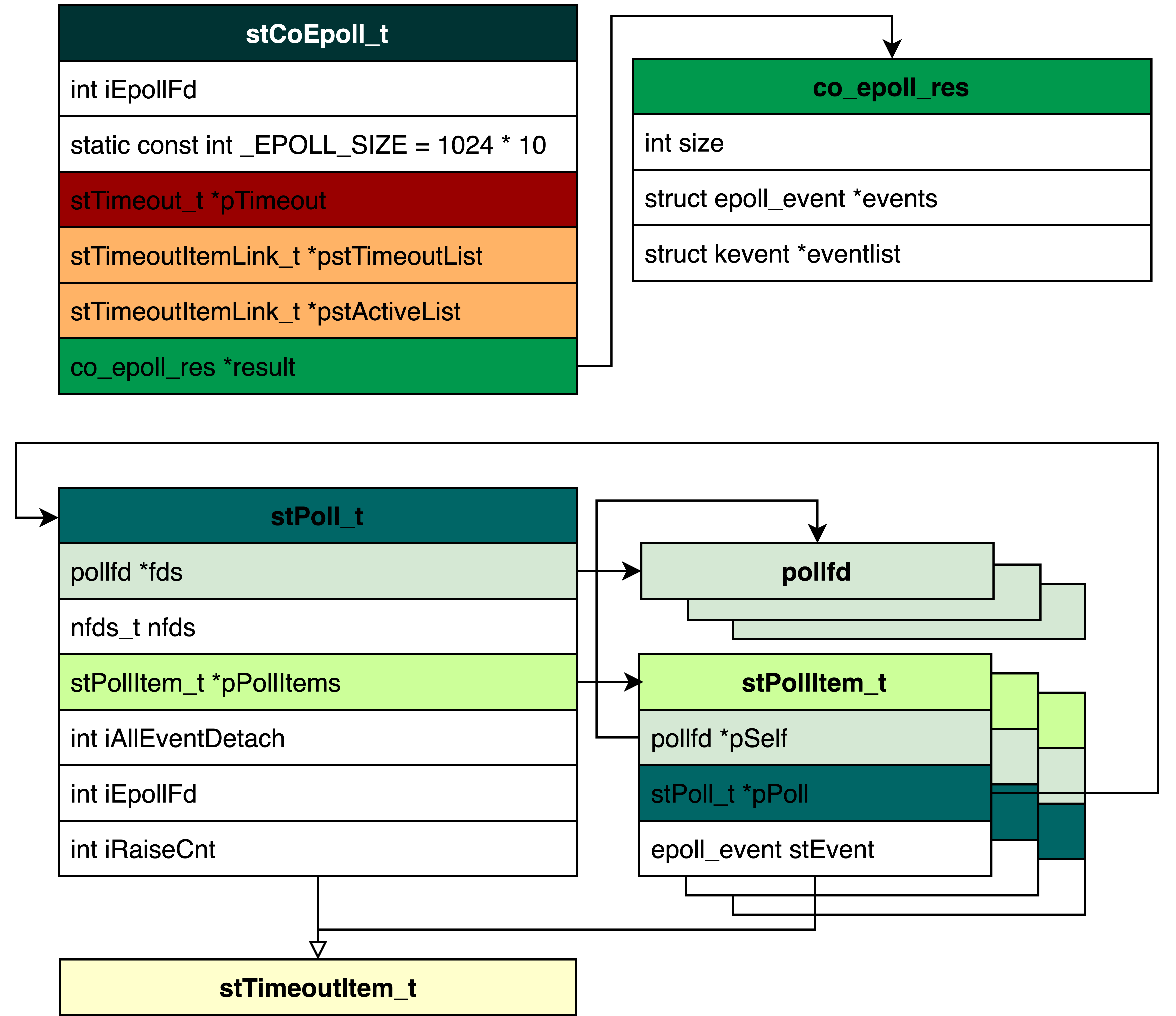
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
|
/* poll内核
* @param
* ctx:epoll句柄
* fds:fd数组
* nfds:fd数组长度
* timeout:超时时间ms
* pollfunc:默认poll
*/
int co_poll_inner( stCoEpoll_t *ctx,struct pollfd fds[], nfds_t nfds, int timeout, poll_pfn_t pollfunc)
{
if (timeout == 0) //poll: Specifying a timeout of zero causes poll() to return immediately, even if no file descriptors are ready.
{
return pollfunc(fds, nfds, timeout); //调用系统原生poll(其实上层poll已经做过检查了,此处无需再做)
}
if (timeout < 0) //poll: Specifying a negative value in timeout means an infinite timeout.
{
timeout = INT_MAX;
}
int epfd = ctx->iEpollFd;
stCoRoutine_t* self = co_self();
//1.struct change
stPoll_t& arg = *((stPoll_t*)malloc(sizeof(stPoll_t))); //分配一个stPoll_t
memset( &arg,0,sizeof(arg) );
arg.iEpollFd = epfd; //此处stPoll_t与stCoEpoll_t进行关联
arg.fds = (pollfd*)calloc(nfds, sizeof(pollfd)); //分配nfds个pollfd
arg.nfds = nfds;
stPollItem_t arr[2];
if( nfds < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) && !self->cIsShareStack) //nfds少于2且未使用共享栈的情况下
{
arg.pPollItems = arr;
}
else
{
arg.pPollItems = (stPollItem_t*)malloc( nfds * sizeof( stPollItem_t ) );
}
memset( arg.pPollItems,0,nfds * sizeof(stPollItem_t) );
arg.pfnProcess = OnPollProcessEvent; //处理函数, 调用co_resume(arg.pArg), 唤醒参数arg.pArg所指协程
arg.pArg = GetCurrCo( co_get_curr_thread_env() ); //处理函数参数, 即当前协程
//2. add epoll
for(nfds_t i=0;i<nfds;i++)
{
arg.pPollItems[i].pSelf = arg.fds + i; //关联stPollItem_t与pollfd
arg.pPollItems[i].pPoll = &arg; //指向所属stPoll_t
arg.pPollItems[i].pfnPrepare = OnPollPreparePfn; //设置预处理
struct epoll_event &ev = arg.pPollItems[i].stEvent;
if( fds[i].fd > -1 ) //fd有效
{
ev.data.ptr = arg.pPollItems + i; //设置stPollItem_t.stEvent.data.ptr指向stPollItem_t
ev.events = PollEvent2Epoll( fds[i].events ); //设置stPollItem_t.stEvent.data.events
int ret = co_epoll_ctl( epfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fds[i].fd, &ev ); //将stPollItem_t.stEvent加入stCoEpoll_t.iEpollFd中
if (ret < 0 && errno == EPERM && nfds == 1 && pollfunc != NULL) //nfds只有一个时,插入epoll失败, 释放掉临时的stPoll_t
{
if( arg.pPollItems != arr )
{
free( arg.pPollItems );
arg.pPollItems = NULL;
}
free(arg.fds);
free(&arg);
return pollfunc(fds, nfds, timeout); //执行原生poll
}
}
//if fail,the timeout would work
}
//3.add timeout
unsigned long long now = GetTickMS();
arg.ullExpireTime = now + timeout;
int ret = AddTimeout( ctx->pTimeout,&arg,now ); //将stPoll_t加入stCoEpoll_t的时间轮
int iRaiseCnt = 0;
if( ret != 0 )
{
co_log_err("CO_ERR: AddTimeout ret %d now %lld timeout %d arg.ullExpireTime %lld",
ret,now,timeout,arg.ullExpireTime);
errno = EINVAL;
iRaiseCnt = -1;
}
else
{
co_yield_env( co_get_curr_thread_env() ); //让出CPU, 等待epoll中的事件发生或超时
iRaiseCnt = arg.iRaiseCnt; //再次回来, 回来前会执行OnPollPreparePfn, 已经将stPoll_t设置好iRaiseCnt, revents, 并从时间轮中删除
}
{
//clear epoll status and memory
RemoveFromLink<stTimeoutItem_t,stTimeoutItemLink_t>( &arg ); //从时间轮中删除
for(nfds_t i = 0;i < nfds;i++)
{
int fd = fds[i].fd;
if( fd > -1 )
{
co_epoll_ctl( epfd,EPOLL_CTL_DEL,fd,&arg.pPollItems[i].stEvent ); //从epoll中删除
}
fds[i].revents = arg.fds[i].revents; //返回已经触发的事件
}
if( arg.pPollItems != arr ) //释放stPoll_t
{
free( arg.pPollItems );
arg.pPollItems = NULL;
}
free(arg.fds);
free(&arg);
}
return iRaiseCnt;
}
|